Author: Pramod Sant
The Indian warehousing sector is at the threshold of a big leap. Market conditions and favourable changes by Govt. are supporting this change.
E-commerce boom, penetration of internet and mobile technology, fast growing middle class with high aspiration is expanding markets and creating demand. In the last few years, Govt. has rolled out many initiatives (like the below) which have helped to boost warehousing demand.
- GST Implementation
- Infrastructure/Industry status to logistics and warehousing allowing FDI
- National Logistics Policy (NLP) with guidelines on warehousing standards
- Make In India
- Production Linked incentive Scheme (PLI)
- Improved EODB ranking
- Road infrastructure and dedicated freight corridors
- Multimodal logistics parks
- Initiatives to Increase use of rail, waterways and coastal shipping
Buoyed by all above factors specially growth of e-commerce sector and expanding Indian manufacturing industry, the Indian warehousing sector has seen PE investment of USD 8 billions in last 5 years. First half of 2022 has already seen investments of USD 1.22 billions. In spite of global slowdown, the Indian warehousing sector has emerged as one of the most attractive investment propositions for investors.
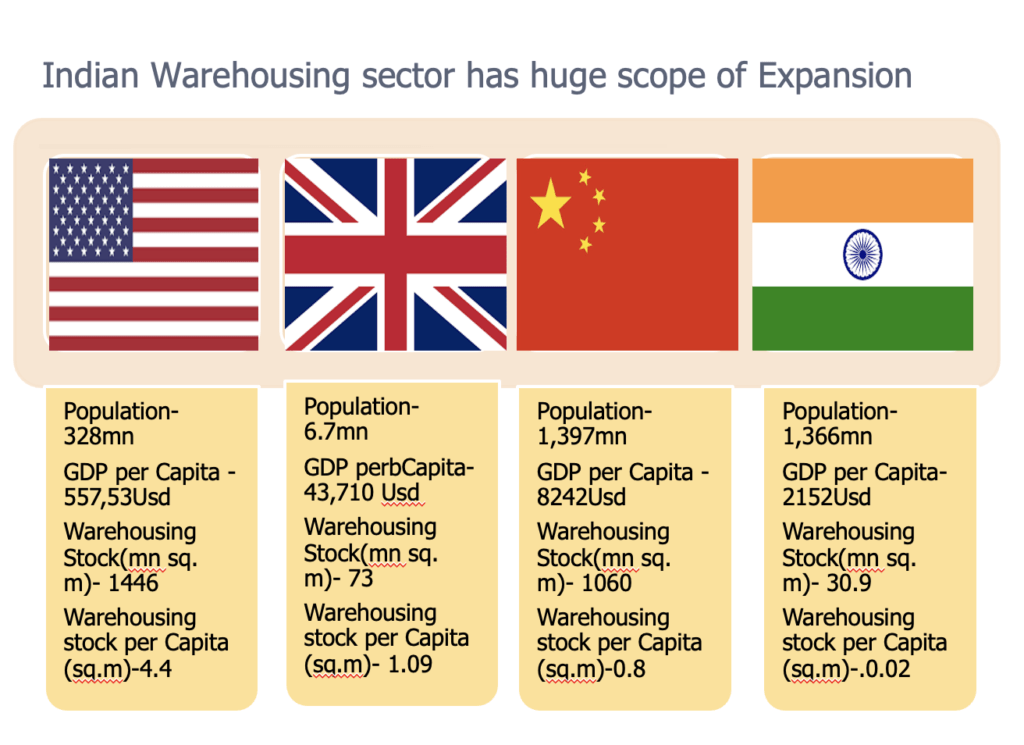
India has very low warehousing stock per Capita (sq.m)-.0.02 compared to China 0.8, UK -1.9 and US 4.4. This data further supplement warehousing growth.

This creates the greatest opportunity for the Indian warehousing sector to embrace new technology, automation, safety and sustainability standards along with green innovations to take a big leap to create our mark globally.
This is an exhaustive subject and I wish to focus on only warehouse automation and technologies which will play a major role.
Warehouse Automation
Indian labour costs are far lower compared to the developed world however we still need to focus on Automation at an early stage. Warehouse automation replaces repetitive tasks with automated systems and eliminates labour-intensive and time-consuming duties. Doing so, in turn, frees workers up to focus on more value-added tasks.
Few additional advantages include:
- Reduce Human Error
- Enhance Material handling coordination
- Boost Inventory Controls
- Improve Customer service
- Improve workplace safety
1. Digital Automation
Following Digital Automation systems will have a major role in any warehouse automation.
Warehouse Management System (WMS): Warehouse management software (WMS) centralizes production-line operations, giving companies greater control over the pace, cost and inventory of the assembly chain. A warehouse management solution will allow production lines to quickly adapt to changes with real-time visibility and access to all relevant data necessary to modify your operation schedule.
There are few important points to be considered while selecting WMS. This includes features (picking, shipping, order management, inventory tracking , labour management, ERP Integration), type of industry (retail, manufacturing, pharma, etc), size of industry (small, medium, large, single /multi locational), deployment key (SaaS platform, on premise platform, SaaS and on premise)
Predictive maintenance software system – connects and analyzes data using sensors like acoustic monitoring, infrared thermography, and vibration analysis. These systems can then take the necessary prevention measures by automatically scheduling corrective maintenance.
Fleet management System/Transport Management systems (TMS) – These systems gather and analyze data from devices mounted on each vehicle, such as speed, engine run time, and fuel use/ TMS summarises data for fleet management to interpret in terms of strategic fleet policies.
2. Physical Automation
Physical automation refers to the use of warehouse automation equipment to reduce employee labour. There are many ways and types by which automation can be done.
Collaborative Robots – or “Cobots” – are robots designed to work side-by-side with human workers.
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) designed to move across your entire warehouse with an onboard operator.
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) – are designed to move automatically without an onboard operator.
Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) -used for store and retrieve cargo in specific locations within a warehouse.
Wearable- augmented reality smart glasses, finger -trigger gloves, and GPS-tracking bracelets. Each is embedded with smart sensors and designed to be worn by warehouse operators. The devices are connected to the web and provide information to guide users on speeding up operations.
Pick-to-light systems and put-to-light systems – direct workers on where to pull order items from storage or where the material should be placed in storage.
Voice picking- is a method for using verbal commands to aid warehouse workers in fulfilling orders. Integrated with a warehouse management system, once an order comes in, the voice picking system will determine the requirements of the order. Then, they’ll verbally convey the information to workers, who receive the commands from a headset.
Automated sortation systems – Automated sortation systems can be of two types, 1) Case sorters, which handle whole cases 2) Unit sorters, which handle individual items
Technologies
Big data and Analysis – Today’s ‘smart’ warehouses automatically gather huge amounts of data, via scanning of goods and through use of sensors on their materials handling and other equipment.
In the past, the resulting datasets would have been overwhelming and too time-consuming to analyze completely. Now, with the availability of powerful analytics solutions, that task has become fast and automatic.
Analytics systems can detect patterns in your data which would otherwise be invisible. More importantly, they present your business with actionable information which allows optimum decision-making and improvements.
Machine Learning (ML) in Warehouse Labor Planning Systems
An example of its application would be an order-picking mobile robot (/what-are-autonomous-mobile-picking-robots) which learns how to handle different items in ways that avoid breakage.
ML can be used to make warehouse labour planning systems much more accurate and efficient compared to traditional approaches based on ‘engineered labour standards’ (ELS). A labour planning system aims to answer questions such as how many workers you will need to fulfil each day’s orders and how long it will take to complete a particular set of tasks.
Automated cross-docking Cross-docking operations in warehouses and distribution centers aim to transfer incoming goods to outbound vehicles with little or no need for storage and with minimal handling.
Mobile Robots as a Service (RaaS) RaaS allows you to use mobile robots without buying them. You could think of it as robot rental, but you only pay when the robots are in action
Computer vision In warehouse – More recently, robots have been developed with the ability to recognize different items by their appearance and to handle them with a ‘smart gripper’. To achieve this, they are equipped with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) capabilities and a vision system using their intelligent computer vision, they can distinguish between a variety of items, mixed up in a container, and locate the one required. They then decide on the best possible route for their picking arm to reach the item, without any collision. Their grabber adjusts to hold it securely but gently, and finally they place it with equal precision next to the other items destined for packing.
Warehouse Drones
personally love these Intelligent drone fleets powered by advanced algorithms linked to cloud-based WMS can assist inventory management inside warehouses.
Warehouse Cleaning
UV Disinfection Robots and Autonomous Floor Scrubbers are a new class of automated mobile cleaning robots that is emerging to safely sanitize and disinfect high-touch indoor warehouses.
Internet of things (IOT)
Although not an emerging technology, RFID sensors continue to be a driving force behind new IoT applications that optimize supply chains and warehouse operations.
Smarter Layouts
Optimizing the layout to improve safety while also increasing efficiency and productivity is difficult, but not impossible. Automation and big data can help.
Automated shelving is only the beginning since a consistent flow of data opens up far more possibilities.
Renewable Energy, Sustainability
Environment is the most discussed topic today and India has advantage when we are creating new warehousing facilities ensuring that they are sustainable. Ensuring that we use maximum renewal energy like solar, wind. Design which will help to ensure min use of lights, material which will help to maintain required temp. This is most important in case of temp controlled warehouses.
With focus on the automation methods and technologies explained above, the Indian warehousing sector can take a leap in the next generation.





