Record demand for container shipping hit 15.9 million TEU in May, as detailed in our report provided by Xeneta. Fronthaul trades are most affected, with the Red Sea conflict and African diversions worsening the situation. Shippers should anticipate rate increases and market volatility.

Global demand for ocean freight container shipping hit a record 15.9 million TEUs in May. This surge highlights significant global transport activity but uneven distribution across supply chains. Importers and exporters must understand the reasons, affected trades, and potential implications of this demand spike.
Below is the data released by Container Trades Statistics:
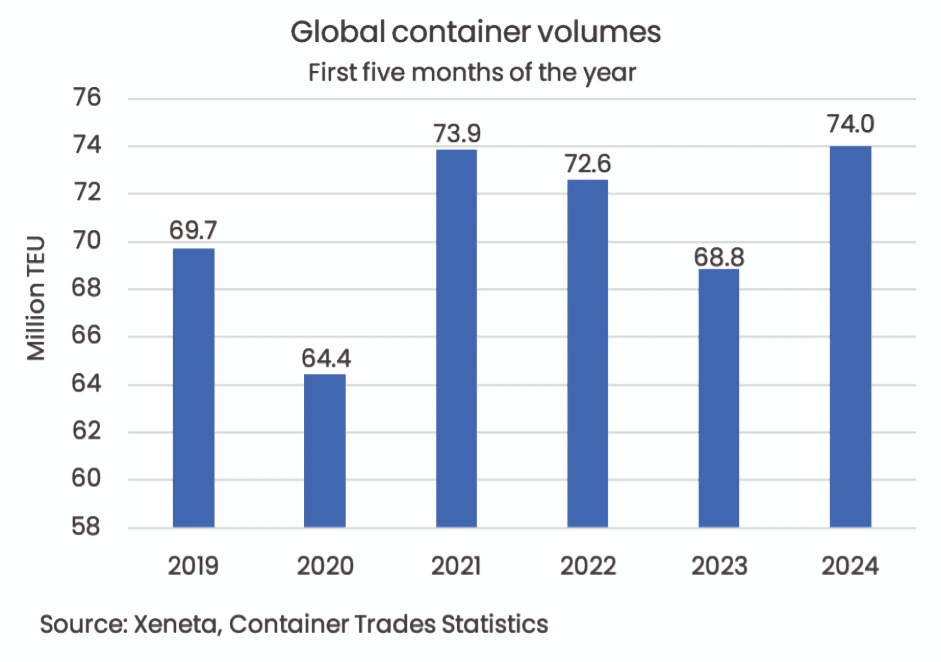
- The 15.9m TEU shipped globally in May beats the previous record of 15.7m TEU set in May 2021.
- 74m TEU were shipped in the first five months of this year, which beats the previous record set in 2021 by 0.15m TEU.
- Volume shipped in the first five months of 2024 is also up by 5.2m TEU compared to the same period in 2023.
- Demand across all global fronthaul trades in May set a new record, rising to 7.3m TEU.
Demand comparison
Demand for ocean freight impacts the market differently based on trade routes. Backhaul trade volumes can rise significantly without major effects due to spare capacity. Conversely, changes in deep-sea fronthaul trades are quickly felt.
In the first five months of 2024:
- Fronthaul volumes rose by 10.4% compared to the same period in 2023.
- Backhaul and intra-regional trades grew by 4.4% and 5.5%, respectively.
- Average spot rates on major backhaul trades to the Far East softened.
- Fronthaul rates from the Far East to North Europe surged nearly 150%.
- Spot rates to the US East and West Coasts increased by 132% and 140%, respectively.
Demand and market conditions
May saw record-breaking demand of 7.3 million TEU across global fronthauls, highlighting the need to monitor demand within the supply context. Fronthaul demand exceeded 7 million TEU in August and December last year, but during a period of falling spot rates and underfilled ships. This was before 1.7 million TEU of new ships were delivered in 2024. The 2024 demand levels would be manageable under normal conditions.
Impact of the Red Sea conflict
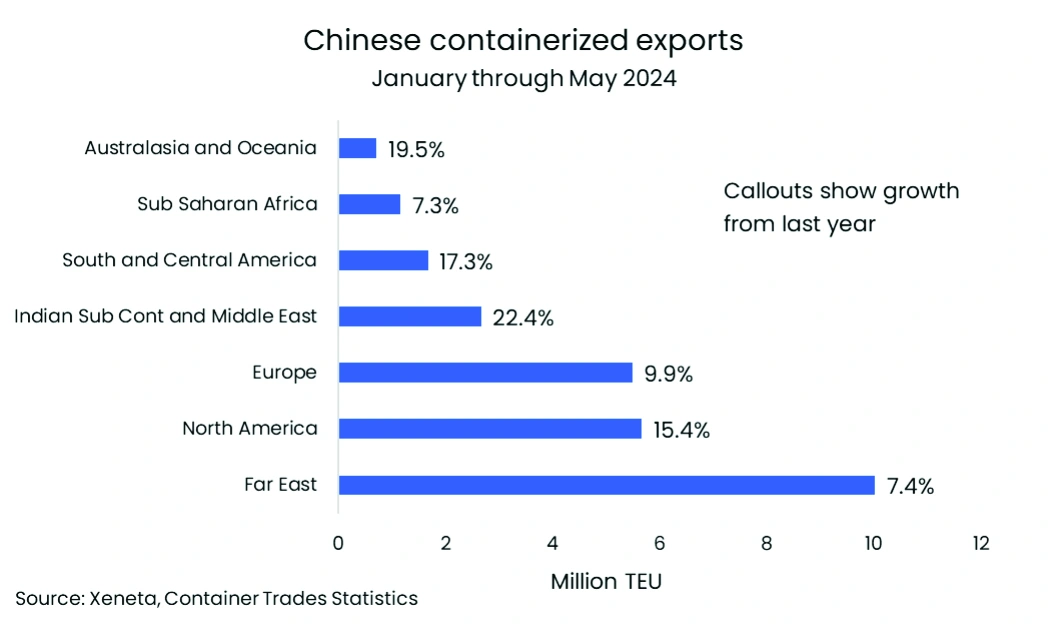
The inability of global ocean container shipping networks to handle 2024’s demand levels is largely due to the Red Sea conflict and subsequent diversions around the Cape of Good Hope. This underscores the need to understand where demand originates. The surge in global volumes in 2024 is mainly driven by record-breaking exports from China. In May, China exported 6.2 million TEU, marking an all-time high, with 853,000 TEU representing intra-China demand.
Chinese exports made up 39% of global container volumes in May. Nearly a quarter of these exports were shipped to Europe and the US East Coast, routes significantly impacted by the longer distances around Africa. TEU-miles, which measure the distance each container travels globally, have risen by 17.9% in 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, primarily due to these extended routes. If carriers had used the Suez Canal, TEU miles would have increased by a lesser 8.6%. This highlights how the Red Sea conflict has intensified demand, further exacerbated by severe port congestion in Asia and Europe.
High demand’s effect on smaller trades
The surge in global demand has allowed carriers to be selective about which containers to load, leading to higher rates and surcharges for shippers and freight forwarders seeking space for their cargo. Carriers are likely to redeploy capacity from smaller trades to more profitable major fronthaul routes, where demand is higher. This shift will reduce capacity and increase rates on smaller trades as well. Shippers relying on secondary trades should be prepared for rising spot rates trickling down from the major trades. The current favourable conditions on smaller trades may not last.
The surge in container demand for 2024 presents both opportunities and challenges. Shippers must navigate rising rates and supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions. Staying informed and adaptable will be essential for managing this evolving market landscape.








